Are you in search of a captivating diamond that fits your budget? If so, exploring the world of ¼-carat diamonds might be just what you need.
In this article, we will delve into everything you need to know about 1/4 Carat (0.25ct) Diamonds. By understanding the key factors that determine a diamond’s quality and value, you’ll be well-equipped to make an informed purchase and delight your loved one with a stunning 0.25-carat diamond ring.
Continue reading to discover more about these exquisite gems!
Diamond Price Chart
DESIGN YOUR OWN ENGAGEMENT RING: START WITH A SETTING OR START WITH A DIAMOND. IT’S REALLY UP TO YOU!
| Shape | Top Quality D/E, FL/IF | Our Recommendation G/H, VS2/SI | The Lower End I/J SI1/SI2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Round | $23,200 | $7,710 | $6,100 |
| Princess | $15,200 | $6,280 | $5,000 |
| Cushion | $15,790 | $5,870 | $3,730 |
| Emerald | $16,050 | $7,760 | $5,140 |
| Oval | $18,950 | $7,390 | $5,760 |
| Pear | $17,800 | $7,580 | $5,710 |
| Marquise | $21,320 | $9,210 | $5,150 |
| Radiant | $20,100 | $7,020 | $4,100 |
| Asscher | $19,610 | $7,720 | $4,360 |

What Is Carat Weight?
The unit of measurement for diamond weight is the metric carat, equivalent to 200 milligrams. When a diamond weighs less than one carat, it is often described in ‘points,’ with each carat divided into 100 points for precise measurement. For instance, a 0.25-carat diamond may be referred to as a ’25 pointer.’ On the other hand, diamonds weighing more than one carat are expressed in carats and decimals. For example, a 1.07-carat diamond would be described as ‘one point seven carats.’
While carat weight affects the price of a diamond, other factors such as color, clarity, and cut also play significant roles in determining its value. It is essential to consider all these aspects collectively, known as the 4Cs, when assessing a diamond’s worth.
It is worth noting the distinction between the terms carat and karat. Carat refers to the weight of the gemstone, while karat is a unit of measure for the fineness of gold.
To measure diamond weight accurately, professionals use electronic micro-balance scales. The weight is typically stated to the fifth decimal place in diamond grading labs, but in the trade, it is often rounded to two decimal places. Rounding rules are followed strictly, rounding up only when the last digit in the fifth decimal place is a 9. This precision is crucial as the price of a diamond is determined by multiplying its carat weight by the price per carat.
It is important to understand that carat weight does not directly correlate with diamond size. Different gemstones have different densities, so stones with the same carat weight may vary in size. Additionally, the cut of a diamond can affect its perceived size. Poorly cut diamonds may hide carat weight beneath a thick girdle, resulting in a smaller visible size. The cut grade of a diamond is thus crucial in determining its overall appearance and value.
In conclusion, relying solely on carat weight to determine a diamond’s size can be misleading. Consider factors like cut grade and actual visible size to make an informed decision about a diamond’s value.

Factors That Influence Diamond’s Price
When an extraordinarily rare 100-carat diamond is discovered, it becomes big news in the diamond trade, and its value soars. Generally, larger diamonds are more valuable due to their rarity, and this is reflected in their price. In fact, the price difference between diamonds of varying carat weights is exponential.
For example, a 1.00-carat diamond will cost significantly more per carat than a 0.25-carat diamond. Similarly, a 2.00-carat diamond will have a higher price per carat compared to a 1.00-carat diamond, and so on.
Now, let’s address the question: How much does a 0.25-carat diamond cost?
A 0.25-carat diamond typically ranges in value from $275 to $440. However, it’s important to note that a diamond’s carat weight is just one factor in determining its worth. Other elements also come into play when assessing a diamond’s value, including:
- Diamond’s cut
- Diamond’s clarity
- Diamond’s color
- Diamond certification
All these factors work together to determine the overall value of a diamond.
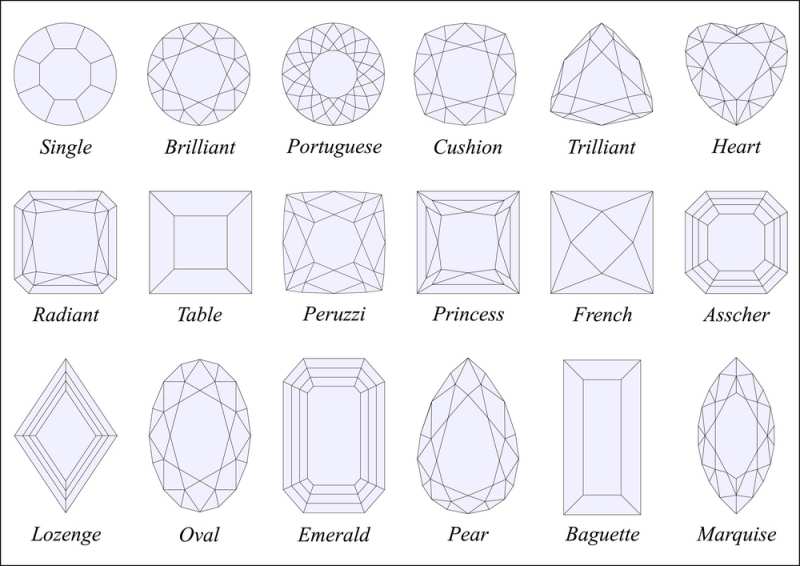
Diamond Cut
Diamonds undergo a meticulous cutting process to enhance their brilliance, fire, sparkle, and overall visual beauty. The cut of a diamond directly influences its light performance, as it determines how light interacts with the stone.
Before being cut and polished, diamonds are in the form of rough stones that have an opaque outer layer, making them difficult to see through. These rough diamonds lack sparkle because they lack facets, which are responsible for reflecting light.
Brilliance and sparkle in a diamond result from its light performance. When light rays enter a diamond, they penetrate the stone, bounce around, reflect within the gem, and eventually return to the viewer’s eyes.
The cutting of a diamond significantly impacts its ability to exhibit light performance. The shape, angles, sizes, and placement of a diamond’s facets determine its sparkle.
Once a diamond is processed, its cut can be graded. For instance, the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) grades a diamond’s cut by precisely measuring the sizes and angles of its facets, including the table, depth, girdle, pavilion, crown, and culet. Additionally, the polish and symmetry of a diamond also contribute to its cut grade.
Each diamond size and shape has an ideal cut proportion. If you seek a perfectly cut diamond, diamond professionals can guide you and present several options that feature ideal proportions.
The cut grade of a diamond can have a significant impact on its pricing, much like other diamond features. Advances in diamond manufacturing technology have allowed for more precise cutting practices. In the case of round brilliant cut diamonds, an Excellent cut grade may command a premium of 5% to 10% over a Very Good cut grade. Similar pricing differentials exist between Very Good and Good cut grades.
Fancy-shaped diamonds do not have GIA-assigned cut grades because they can have various shapes, widths, and lengths while still maximizing the stone’s sparkle.
When choosing a diamond, the cut is generally regarded as the most important factor. Excellent cut diamonds are the best but also the most expensive. Very Good cut diamonds offer great value, with subtle differences in brilliance that become apparent when compared side by side. It is advisable to prioritize a higher cut grade whenever possible.
Fancy-shaped diamonds offer more flexibility as beauty is subjective. However, it is generally safe to opt for one grade lower in cut for fancy-shaped diamonds, although ideally cut fancy-shaped diamonds are rare.
Ultimately, the choice is yours, and it is essential to consider other factors that influence a diamond’s beauty and price. Determine which attributes matter most to you and make an informed decision based on your preferences.

Diamond Color
Both natural and lab-grown diamonds come in a wide range of colors. Traditional engagement rings often feature white diamonds, which are colorless stones. However, there are also fancy colored diamonds available, showcasing vibrant shades like pink, yellow, and green.
Color is a natural characteristic of diamonds. As these gems form deep beneath the Earth’s surface over millions of years, trace elements can introduce a yellowish or brownish tint to the diamonds. It is more common for diamonds to exhibit some level of color, which can vary in tone and saturation, rather than being completely colorless.
Diamond color grading involves assessing the stone’s body color when viewed face down against a pure white background. Diamond experts compare the gem to master stones with different color shades to determine its grade. If a stone exhibits more yellow tint than one shade but less than another, it will receive a grade within that range.
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) has established a standardized color grading scale for diamonds, ranging from D (highest color grade) to Z (lowest color grade). In diamond grading, color is determined by the absence of color in the stone. The less color a diamond has, the higher its grade.
Colorless diamonds tend to sparkle more than those with a yellowish or brownish tint because the subtle color distracts the eye from perceiving the sparkle.
When considering the best diamond color for your 0.25-carat diamond, it depends on your preferences. Here are some options to consider:
Diamond Color D-F: Colorless – Stones in this range exhibit minimal traces of color that can only be detected by professional gemologists. These diamonds typically need to be compared to higher or lower graded stones to accurately discern the color. Less than 1% of all gem-quality diamonds fall into this color range.
Diamond Color G-J: Near Colorless – Gems in this range possess a slight amount of color that trained eyes can identify. G/H color diamonds are popular because they strike a balance between minimal color and value.
I/J color diamonds may have minor distractions in sparkle, but they still exhibit brilliant sparkle and offer good value. This color range represents the top 15% of all gem-quality diamonds.
Diamond Color K-M: Faint – Diamonds with these color grades tend to have faint yellow or brown tones. The color may slightly dull the gem’s sparkle, and it may be noticeable when inspected in jewelry. However, there are ways to minimize this effect. These diamonds represent the top 40% of all gem-quality diamonds.
Ultimately, the choice of diamond color depends on your personal preference and the desired balance between colorlessness and value.
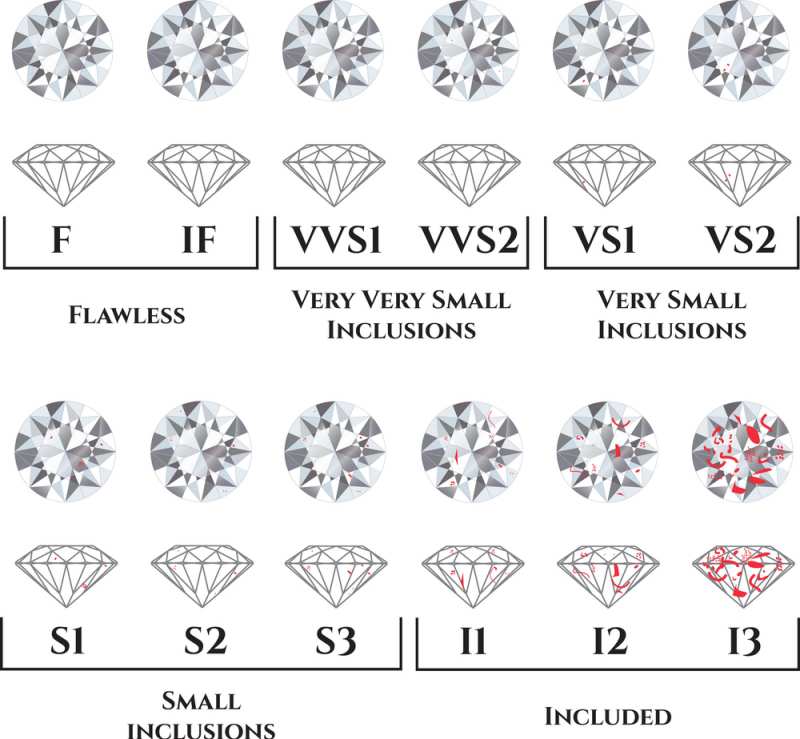
Diamond Clarity
The formation of natural diamonds occurs when carbon is subjected to extreme conditions of high heat and pressure deep beneath the Earth’s crust. This process can result in the development of various internal flaws known as “inclusions” as well as external flaws referred to as “blemishes.”
Assessing the clarity of a diamond involves evaluating the number, size, nature, and location of these blemishes and inclusions and understanding how they influence the overall appearance of the diamond.
When determining the ideal clarity grade for your 0.25-carat diamond, it’s important to note that no diamond is entirely flawless. The closer a diamond comes to being free of imperfections, the higher its clarity grade.
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) has established a diamond clarity scale that comprises six categories, some of which are further divided, resulting in a total of 11 specific clarity grades:
- Flawless (FL): No inclusions or blemishes are visible under 10x magnification.
- Internally Flawless (IF): No inclusions are visible under 10x magnification.
- Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2): These diamonds have slight inclusions that are challenging to see under 10x magnification, even for an experienced grader.
- Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2): These diamonds have inclusions that are detectable with effort under 10x magnification but can be considered minor.
- Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2): Inclusions can be observed under 10x magnification in these diamonds.
- Included (I1, I2, and I3): Diamonds in this clarity range exhibit obvious inclusions under 10x magnification, which may affect transparency and brilliance.
Many internal and external flaws are too small to be detected by anyone other than a professional gemologist. While a VS1 and an SI2 graded diamond may appear identical to the naked eye, they differ significantly in terms of overall quality.
Hence, an accurate evaluation of diamond clarity conducted by an expert is crucial. Understanding the true meaning of diamond clarity can help you grasp the factors that influence a diamond’s quality and price.
Clarity differences in diamonds tend to have a more substantial impact on pricing compared to color differences since the clarity scale is smaller. The price variations between clarity grades can be quite significant, particularly as the highest clarity grades are much rarer, resulting in large price jumps.
Price differences can range from 15% to 25% between clarity grades, while differences within the same clarity category can range from 5% to 15%. It’s essential to remember that no two stones are alike, meaning that no two diamonds with the same clarity grade are identical.
Given the subjective nature of determining a diamond’s clarity grade, factors such as the size, number, location, and type of imperfection can affect the stone’s price. For instance, an SI1 graded diamond with a visible black crystal at the center of the table will be considerably less expensive than a diamond with the same clarity grade but featuring an eye-clean feather in a corner that can be covered by a prong.
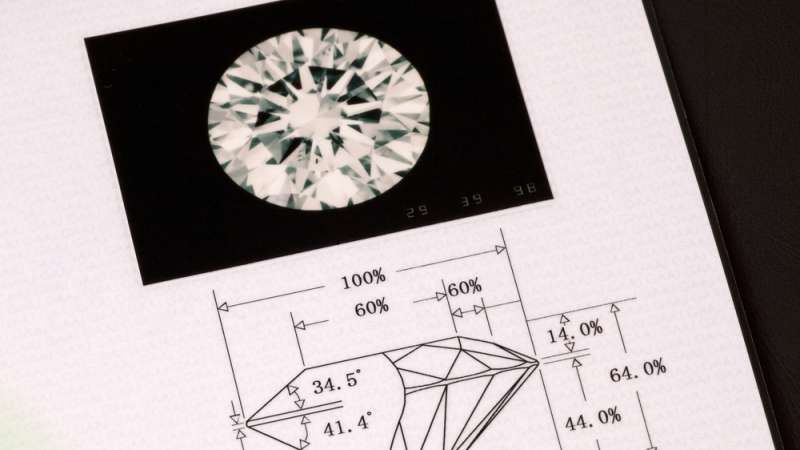
Diamond Certification
While the distinctions in diamond characteristics mentioned earlier may be subtle, the differences in price are not. Since assessing diamonds requires a high level of expertise, it is crucial to be aware of your stone’s precise attributes and characteristics.
Given the considerable variation in pricing, it is important to avoid purchasing a diamond that is advertised as having certain qualities only to receive something entirely different. This is where diamond certificates play a significant role. These certificates standardize the characteristics of diamonds, providing you with clear information about what you are getting for the money you have paid. In essence, they offer consumer protection on a global scale.
Many diamond buyers wonder why some gems come with certificates, charts, or extensive documentation upon purchase, while others only come with a receipt.
While you can request diamond-related information before purchasing a stone and obtain copies of information for the one you choose, more detailed certificates and grading reports are typically reserved for gems that have received official certification.
Gemological institutions carefully evaluate, compare, and grade gems for quality and consumer demand, issuing certificates for these stones. Non-certified diamonds may come with ratings or accompanying documentation, but they have not obtained an official certificate from a recognized diamond grading lab like the GIA.
Do you need diamond certification for your 0.25-carat diamond?
The most apparent advantage of purchasing a certified diamond is the assurance that you are receiving what you paid for in terms of exceptional quality and beauty.
On the other hand, the main disadvantage of purchasing a diamond with a certificate is the additional cost associated with certified gems. While you will likely pay more for a certified diamond, it is worth every penny for discerning consumers who prioritize quality and authenticity.

0.25-carat Diamonds and Jewelry
When selecting jewelry, it is crucial to carefully balance your budget, style, and expectations. Even though 0.25-carat diamonds are generally small, they can still create beautiful jewelry pieces.
0.25-carat Diamond Rings
If your budget for a diamond ring is under $1,000, you will likely be looking at stones around 0.25 carats. Although these round diamonds are small in size, they can still exhibit incredible brilliance.
0.25-carat Diamond Studs
Diamond studs are typically sold based on their total carat weight, which means you need to divide the carat weight in half to determine the weight of each stone for each ear.
At 0.25 carats, the diamonds will be relatively small. However, this size is perfect for a gift for a child or for those who prefer subtle and understated jewelry.
0.25-carat Diamond Pendants
Choosing the right size for a pendant can be tricky as it depends on individual style preferences and neck sizes. If you are purchasing a pendant for yourself, it is helpful to try on different sizes at a jewelry store to see what suits you best.
With a 0.25-carat diamond, a round brilliant cut stone will have a diameter of approximately 4 mm. This makes it an excellent option for a pendant that is noticeable but not overly flashy. It can be the perfect size for versatile jewelry suitable for both formal and casual occasions, especially in petite settings.

Bottom Line
Purchasing a diamond, especially one weighing less than one carat, can feel overwhelming. However, by following the recommendations we’ve discussed, you can ensure you get the best value for your next 0.25-carat diamond purchase.
Always prioritize the cut quality of the diamond as it is the most important factor. Then, consider the clarity and color, as they also play a significant role in the diamond’s quality and overall appearance.
Lastly, although 0.25-carat diamonds are relatively small, they can still create exquisite jewelry pieces. Therefore, don’t forget to choose a suitable jewelry setting that will enhance the brilliance and beauty of your 0.25-carat diamond!


